Intrigued by the potential of automating your IoT data processing? Mastering remote IoT batch jobs on AWS is not just beneficial; it's becoming essential for staying competitive in the rapidly evolving landscape of connected devices.
The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to revolutionize industries, generating vast amounts of data from a multitude of devices. Managing and processing this data efficiently is a critical challenge, and that's where remote IoT batch jobs on Amazon Web Services (AWS) step in. These jobs provide a powerful and scalable solution for automating data processing tasks, enabling organizations to derive valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. But what exactly are these jobs, and how can you effectively leverage them?
A remote IoT batch job example is essentially a predefined task that runs automatically on AWS to process large volumes of IoT data. Think of it as a digital assembly line where each step is carefully orchestrated to transform raw data into actionable information. These jobs are designed to handle the scale and complexity of modern IoT deployments, from simple data aggregation to complex analytics and machine learning tasks. This article delves into the nuances of setting up and managing remote IoT batch jobs on AWS, offering practical examples and expert advice. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced professional, this guide will provide valuable insights into leveraging AWS for IoT batch processing.
- Barron Trump Songs Fact Vs Fiction The Ai Buzz
- Trevor Noahs Love Life Minka Kelly Dating History More
Benefits of Remote IoT Batch Jobs
- Automation: Automates repetitive data processing tasks, freeing up valuable human resources.
- Scalability: Easily handles increasing data volumes as your IoT deployment grows.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Optimizes resource utilization, reducing infrastructure costs.
- Efficiency: Processes data in parallel, significantly reducing processing time.
- Reliability: Ensures consistent and reliable data processing operations.
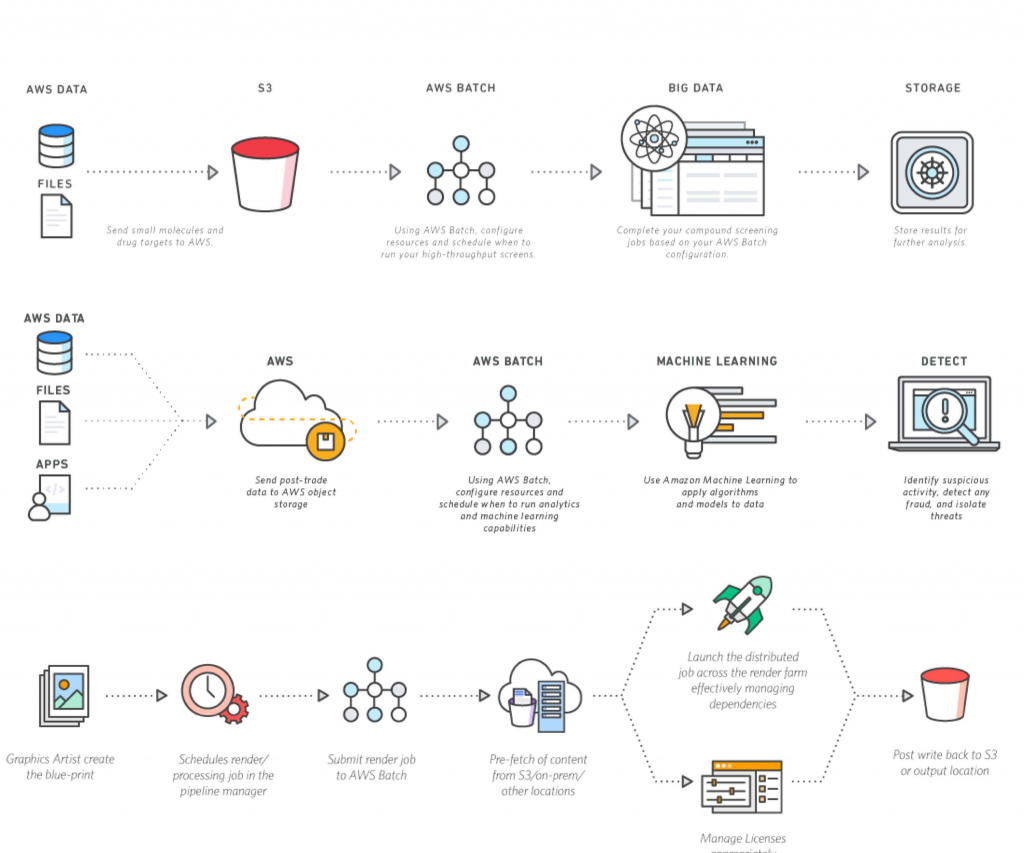
With the rise of IoT devices and remote data collection, understanding how to implement batch jobs on AWS can significantly enhance operational capabilities. Let's explore how to build and deploy them. First of all, we need to understand key components. Setting up a remote IoT batch job on AWS generally involves several key components working in tandem: a data source (e.g., IoT devices sending data to AWS IoT Core), a storage service (e.g., Amazon S3 for storing raw data), a processing service (e.g., AWS Lambda, AWS Batch, or Amazon EMR for processing data), and a database or data warehouse (e.g., Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Redshift, or Amazon Athena for storing processed data and insights). Consider AWS IoT Core as the central nervous system for your IoT devices, enabling them to connect to the AWS cloud securely. When a device sends data, IoT Core can trigger an action. Next, the data is often stored in Amazon S3, a highly scalable and durable object storage service, and after this process services like AWS Lambda or AWS Batch can then be triggered to process this data. Lambda is an event-driven, serverless compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. AWS Batch enables you to run batch computing workloads on AWS. Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce) provides a managed Hadoop framework for processing large datasets. Lastly, processed data can then be stored in a database like DynamoDB, a fast and flexible NoSQL database service, or a data warehouse such as Amazon Redshift or Amazon Athena, which provide advanced analytics and reporting capabilities.
Setting Up the AWS Environment
Before you begin building your remote IoT batch jobs, you'll need to set up the necessary AWS environment. This involves several key steps:
- AWS Account: Create an AWS account if you don't already have one.
- IAM Roles: Configure Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles to grant the necessary permissions to your processing services. For example, your Lambda functions or Batch jobs will need permissions to access S3 buckets, DynamoDB tables, etc.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Configure your processing services to run within a VPC for added security and network isolation.
- Monitoring: Set up monitoring and logging using services like Amazon CloudWatch to track the performance and health of your batch jobs.
Step-by-Step
Lets walk through a simplified example of setting up a remote IoT batch job to process temperature data from IoT devices. This is a common use case.
- Trump Iq Test Results Former Nyma Employee Closet Discovery
- Barron Trump Singing On Agt Decoding The Ai Videos
- Data Ingestion: IoT devices send temperature readings to AWS IoT Core, which in turn publishes the data to an MQTT topic.
- Data Storage: A rule in IoT Core triggers a Lambda function whenever a new message is published to the MQTT topic. This Lambda function stores the raw temperature data in an Amazon S3 bucket.
- Batch Processing: At regular intervals (e.g., hourly or daily), AWS Batch is triggered to process the data stored in the S3 bucket.
- Data Transformation: The AWS Batch job runs a custom processing script (e.g., written in Python) that reads the data from S3, calculates average temperature, and identifies any anomalies.
- Data Storage and Analysis: The processed data, along with any anomalies, is stored in Amazon DynamoDB for easy retrieval and analysis. You can then use Amazon QuickSight or other tools to visualize the data and gain insights.
This streamlined example provides the foundational steps for setting up remote IoT batch jobs, this approach allows you to build more complex systems as your needs evolve. As your needs grow, you can expand this example to include more advanced data transformations, machine learning models for anomaly detection, and real-time dashboards for monitoring your IoT data.
Best Practices to Avoid Common Pitfalls
While remote IoT batch jobs offer many benefits, they also come with their own set of challenges. Successfully implementing these jobs requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to help you avoid common pitfalls.
- Optimize Data Storage: Choose the right storage solution for your data. For example, Amazon S3 is ideal for storing large volumes of raw data, while Amazon DynamoDB is suitable for storing processed data that needs fast access.
- Implement Error Handling: Ensure your processing scripts and jobs include robust error handling to gracefully handle failures and data inconsistencies. This can include retries, logging, and alerting.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor the performance of your batch jobs, including processing time, memory usage, and throughput. Use CloudWatch to set up alerts for any performance bottlenecks.
- Secure Your Jobs: Implement robust security measures to protect your data. This includes using encryption at rest and in transit, implementing access controls, and regularly auditing your security configuration. AWS provides advanced encryption, access control, and monitoring capabilities that ensure the integrity and safety of your IoT ecosystem.
- Version Control: Use version control (e.g., Git) to manage your processing scripts and configurations. This makes it easier to track changes, revert to previous versions, and collaborate with others.
- Test Thoroughly: Test your batch jobs thoroughly before deploying them to production. This includes testing different data volumes, data formats, and error conditions.
- Optimize for Cost: Continuously monitor your costs and optimize your batch jobs for cost-effectiveness. This includes choosing the right instance types, optimizing your code, and using spot instances where possible.
Challenges and Solutions in Remote IoT Batch Jobs
Navigating the landscape of remote IoT batch jobs often presents a unique set of challenges. Recognizing and addressing these issues proactively is critical for ensuring the successful implementation and operation of these systems. Here's a breakdown of common challenges and corresponding solutions:
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Data Volume and Velocity: Managing the influx of data from numerous IoT devices at high speeds. | Employ scalable storage solutions (e.g., S3), optimize data partitioning strategies, and use parallel processing techniques like AWS Batch or EMR. |
| Data Quality: Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data ingested from devices. | Implement data validation, cleansing, and transformation processes within your batch jobs to identify and correct errors. |
| Scalability: Scaling the processing capacity to handle peaks in data volume. | Utilize services such as AWS Lambda and AWS Batch, which automatically scale to meet demand. Ensure proper resource allocation and optimization. |
| Security and Compliance: Protecting sensitive data and adhering to regulatory requirements. | Implement end-to-end encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Leverage AWS security services, like IAM and KMS. |
| Complexity: Dealing with the intricacy of setting up and managing distributed processing workflows. | Adopt a modular approach, using infrastructure-as-code tools (e.g., CloudFormation, Terraform) to simplify deployments and automate tasks. |
| Cost Optimization: Managing expenses associated with data storage, processing, and network transfer. | Monitor resource utilization, utilize cost-effective services, and optimize code for efficiency. Employ strategies such as spot instances and reserved instances when applicable. |
| Monitoring and Alerting: Tracking the performance of jobs, identifying bottlenecks, and receiving notifications about issues. | Integrate with AWS CloudWatch to monitor performance metrics, set up alarms, and receive notifications when issues arise. Implement logging throughout your processes. |
| Integration: Connecting various services (e.g., data sources, processing engines, databases) to form a cohesive system. | Employ managed services like AWS Glue, AWS DataSync, and AWS IoT Core to simplify data movement and synchronization. Design your system with clear API contracts. |
Security Considerations
How secure are remote IoT batch jobs when implemented with AWS? Remote IoT batch jobs implemented with AWS are highly secure, thanks to AWS's robust security features and compliance with industry standards. AWS provides advanced encryption, access control, and monitoring capabilities that ensure the integrity and safety of your IoT ecosystem. The following points are important.
- Data Encryption: AWS offers encryption at rest and in transit to protect data confidentiality.
- Access Control: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows you to control access to resources and data based on the principle of least privilege.
- Network Security: Utilize Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) to isolate your batch jobs and data from the public internet.
- Compliance: AWS adheres to various industry standards and certifications, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001, providing a secure environment for your batch jobs.
Leveraging AWS Services for IoT Batch Processing
Understanding how remote IoT batch jobs work within the AWS ecosystem is crucial for leveraging modern technology effectively. The Internet of Things (IoT) continues to revolutionize industries, with remote IoT batch jobs playing a pivotal role in automating data processing tasks.
Several AWS services are particularly well-suited for building and running remote IoT batch jobs. These services, when used together, offer a comprehensive solution for ingesting, processing, storing, and analyzing IoT data.
- AWS IoT Core: This is the foundation for connecting your IoT devices to the AWS cloud. It provides secure and scalable bi-directional communication between your devices and the cloud.
- Amazon S3: A highly scalable object storage service ideal for storing raw IoT data, processed datasets, and other files.
- AWS Lambda: A serverless compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. It's perfect for event-driven processing, such as reacting to data updates from IoT devices or pre-processing raw data.
- AWS Batch: A batch computing service that allows you to run batch jobs on AWS. It automatically provisions compute resources and manages the job queue, making it easy to process large volumes of data.
- Amazon EMR (Elastic MapReduce): A managed Hadoop framework that provides powerful processing capabilities for large datasets.
- Amazon DynamoDB: A fast and flexible NoSQL database service for storing processed IoT data and real-time analytics.
- Amazon Redshift and Amazon Athena: Data warehousing and query services that enable in-depth analysis and reporting on your IoT data.
- Amazon CloudWatch: A monitoring service that enables you to track the performance of your batch jobs, set alarms, and gain insights into your infrastructure.
- Viral Pastor Brandon Biggs Predicted Trump Assassination Attempt
- Love After Lockup Daontes Drama Baby News